NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS
NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT PROCESS
As markets and
customer preferences change companies adapt to insure success. Adaptations
usually are made to capitalize on markets and expertise a firm has developed
over its life.
Some adaptations
are limited to updating packaging or marketing approaches or finding new uses
for established products.
There are
occasions where new products are needed in order to meet new customer needs or
address a disruptive market innovation.
When addressing
changing market needs and market disruptions it is necessary to find good ideas
and then have a process to evaluate and narrow the field to the ideas most
likely to succeed.
Generating new product ideas
The first step in
generating good ideas that will further develop the markets and expertise that
defines the firm is to clearly articulate the job customers are hiring the firm
to perform.
Here it is
important not to be too restrictive in the focus of the definition. It is
probably better for an owner of a baseball team to define his firm’s job as sports
entertainment as opposed to the more focused definition of professional
baseball.
Once the job the
customer has hired the company to perform is defined then it will be easier to
identify new product ideas that are based on the firm’s strengths.
There are several
methods to develop new product ideas that are very useful such as brainstorming,
market research and product attribute modeling.
Brainstorming is
widely used and involves getting key employees (and sometimes customers)
together to find solutions to challenges facing the firm. The key to successful
brainstorming is good note taking, allowing all ideas to be presented without
negative feedback and encouraging all participants to contribute without
letting a few dominate the exercise. This cannot be be enhanced with AI. Ince you have identified the job to be done, ask AI to list product or services that might be offered. You will find that there will be numerous possibilities.
Market research
can be the result of research surveys designed to uncover market opportunities.
This research involves current customers, individuals with characteristics
similar to current customers or a random selection of individuals. Examining a
firms records and reviewing sales staff information on the market and the
competition can also provide solid market research.
Product attribute
modeling is a unique way of generating new product ideas by choosing a job the
company is hired to perform and describe the absolute worst outcomes. After identifying
the bad outcomes, participants go back through the exercise and determine what
actions could be taken to eliminate the negative outcomes. For example if a
company made suitcases an exercise might be to list all of the negative
attributes for suitcases (such as not fitting in overhead bins in aircraft,
wheels that wobbled, instability etc.). The follow up exercise would be to
create a suitcase that addressed all of the negative attributes.
The best idea
generation will likely come from a program that involves all of the idea
generation techniques, First, market research, then brainstorming based on the
research and finally product attribute modeling.
Identifying the best ideas
After the idea
generation process there are likely to be a number of ideas that are
attractive. The challenge is to find a way of objectively identifying those
ideas that have the most promise.
For this process
it is important to assemble a committee of key employees from each part of the
business. The committee should have members from sales, IT, finance,
accounting, production, R&D, and engineering. This structure allows any
idea to have the insights of the various parts of the organization. The
committee should be led by an individual that can keep the group generating
customer focused ideas and prevent efforts to kill product ideas because they
don’t fit with current thinking.
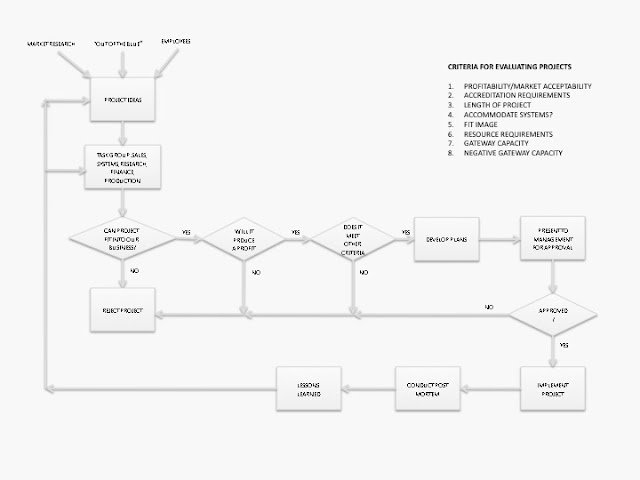
When evaluating
new product ideas there should be specific criteria identified that the new
product must meet before moving to the next level of consideration. A list of
evaluation criteria might look like the following:
1. Profitability/market acceptability
- will the product generate a profit and a market?
2. Accreditation requirements – Does the product meet industry and legal
standards?
3. Length of project – Can the product be introduced in an acceptable time
frame?
4. Accommodate systems – Does the new product make use of current systems
or will new ones need to be developed?
5. Fit Image – Does the product fit the image the firm wishes to project?
6. Resources – is the new product resource and capital intensive?
7. Gateway capacity – Does this product lead to the possibility of new
products or businesses being developed?
8. Negative Gateway capacity – Does this product have the potential of
damaging other aspects of the operation?
9. Customer acceptance – will the customer accept this product over others
offered in the market?
If product ideas
successfully meet all of the criteria then product ideas can be chosen to move
forward to a product planning process. Those chosen as having the highest
priority should best meet all of the criteria with the least organizational
expense.
Comments
product development